-
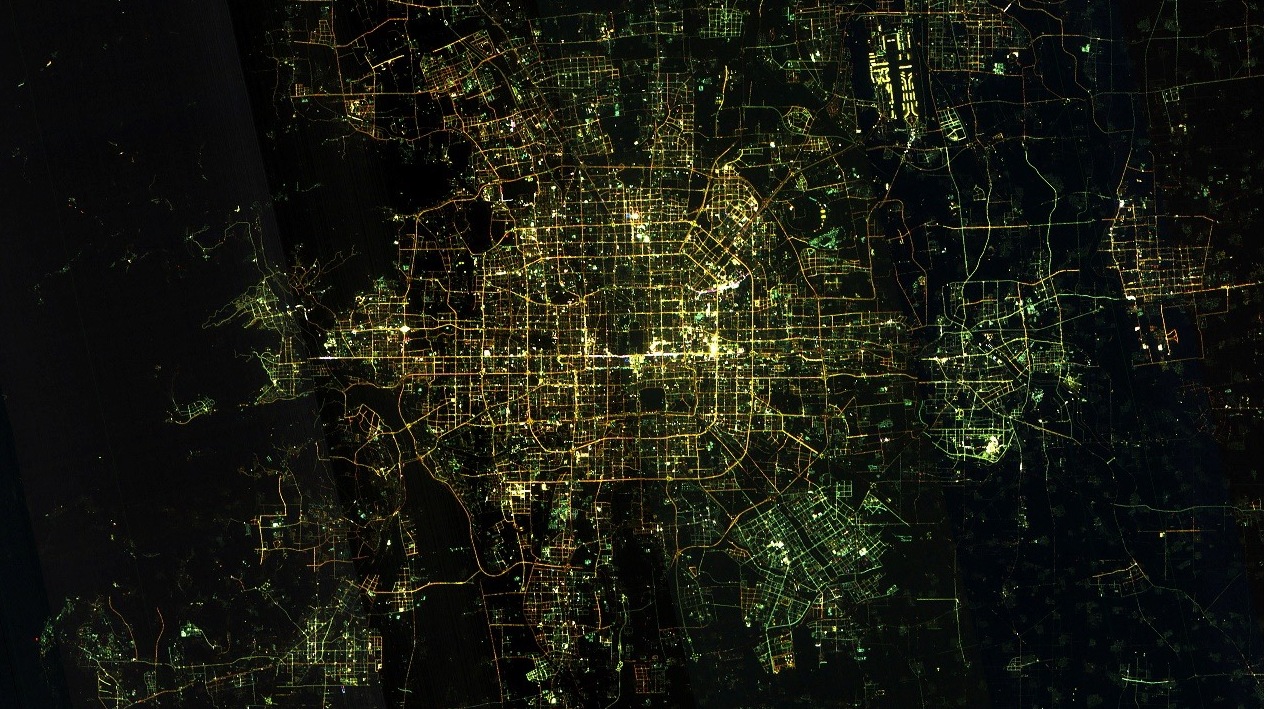 China Unveils First Images Taken by Satellite SDGSAT-1
China Unveils First Images Taken by Satellite SDGSAT-1A group of images taken by Chinese satellite SDGSAT-1 to help meet UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) were unveiled in Beijing on Monday.
20 Dec 2021 -
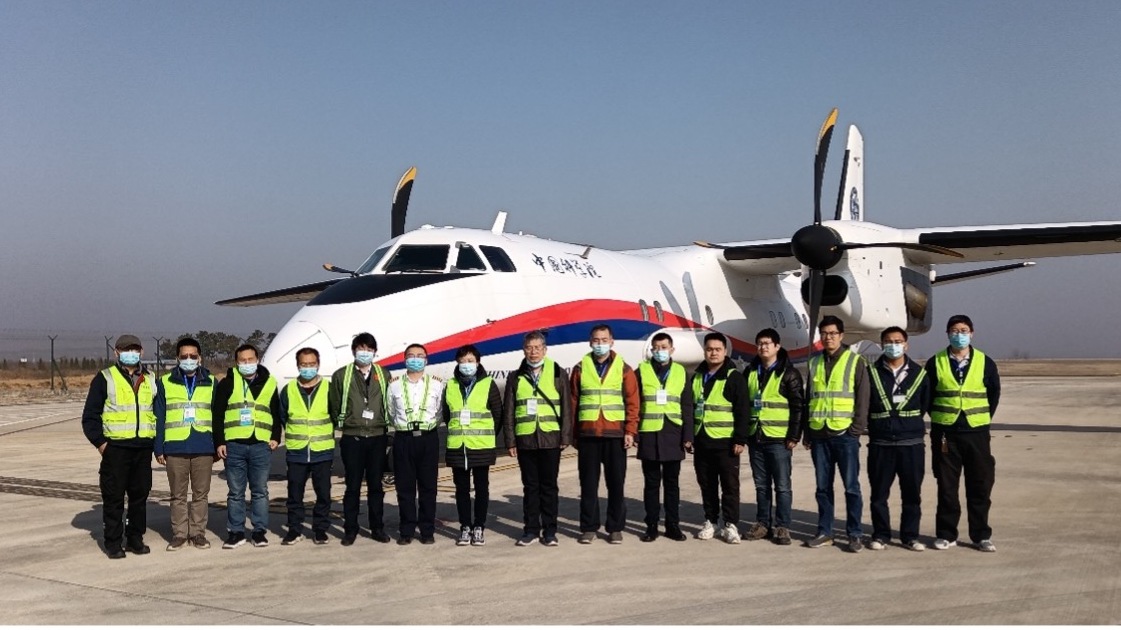 Airborne Remote Sensing Experiment Completed on Home-grown MA60 Aircraft
Airborne Remote Sensing Experiment Completed on Home-grown MA60 AircraftWith the landing of a MA60 aircraft, a comprehensive remote sensing experiment wrapped up in Rizhao, Shandong Province on November 30, 2021.
10 Dec 2021 -
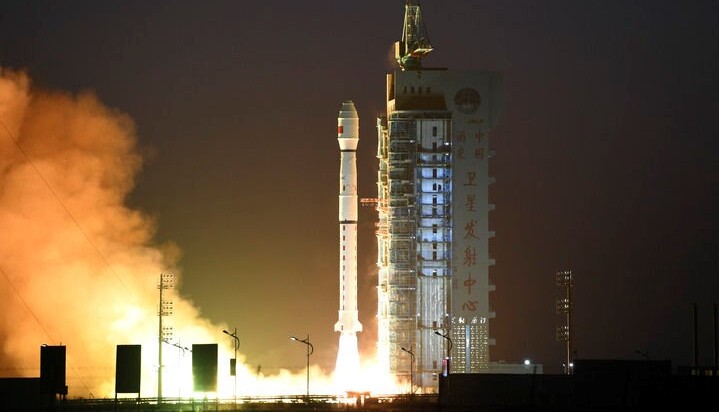 GF-3 02 Satellite Launched to Boost Land-Sea Observations
GF-3 02 Satellite Launched to Boost Land-Sea ObservationsGF-3 02 satellite is equipped with multi-polarized C-band SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) which was developed by a research team from the Aerospace Information Research Institute (AIR), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS).
25 Nov 2021 -
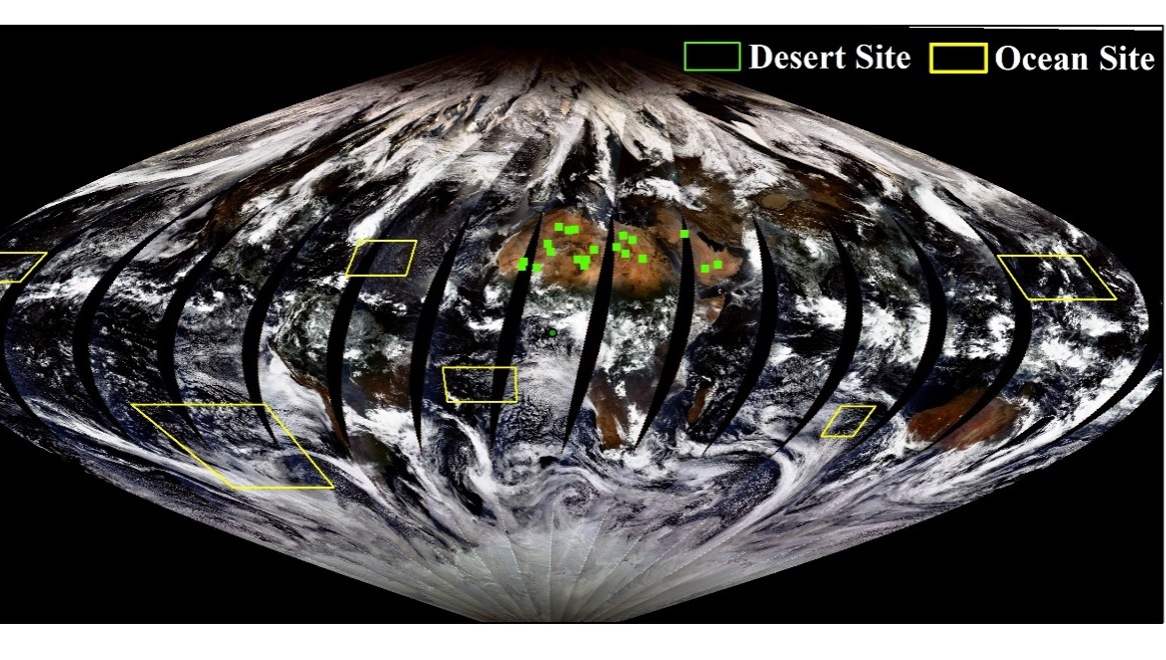 In-orbit Test Conducted on Polarization Crossfire Sensor Suite onboard China's Hyperspectral Earth Observation Satellite
In-orbit Test Conducted on Polarization Crossfire Sensor Suite onboard China's Hyperspectral Earth Observation SatelliteAn in-orbit test of the polarization crossfire (PCF) sensor suite onboard GaoFen-5 (02), a hyperspectral Earth Observation satellite launched on September 7, 2021, was carried out by a joint research team led by Prof. LI Zhengqiang from the National Engineering Laboratory for Satellite Remote Sensing Applications under the Aerospace Information Research Institute (AIR), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS).
15 Nov 2021 -
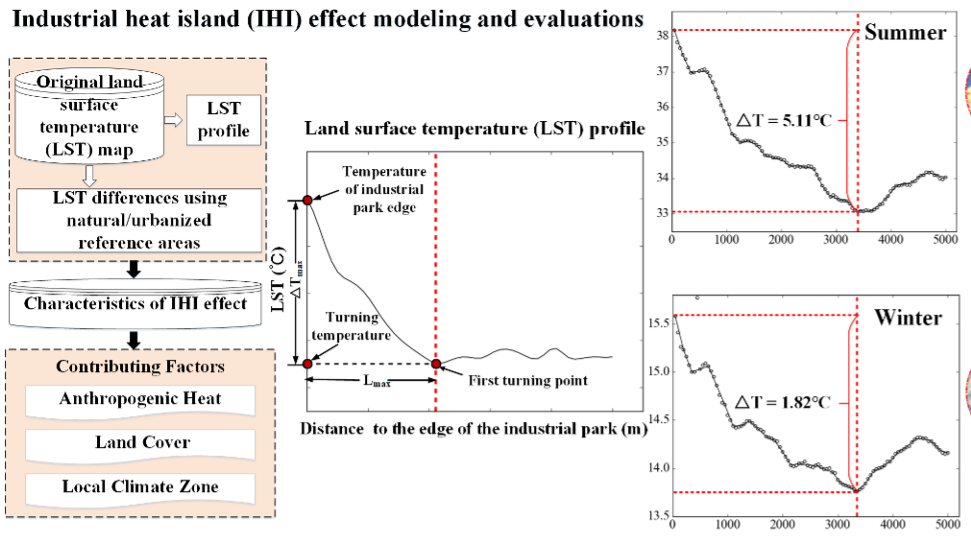 New Evidence, Quantitative Methods, and Contributing Factors of Industrial Heat Island Effects
New Evidence, Quantitative Methods, and Contributing Factors of Industrial Heat Island EffectsA research team led by Prof. MENG Qingyan from the National Engineering Laboratory for Satellite Remote Sensing Applications under the Aerospace Information Research Institute (AIR), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), has published a paper on the Environmental Pollution on the urban intra-heat island effects. The paper tries to provide evidence, quantitative methods, and contributing factors from a spatiotemporal analysis of top steel plants in China? Prof. MENG Qingyan and doctoral candidate HU Die are the co-first authors.
17 Nov 2021 -
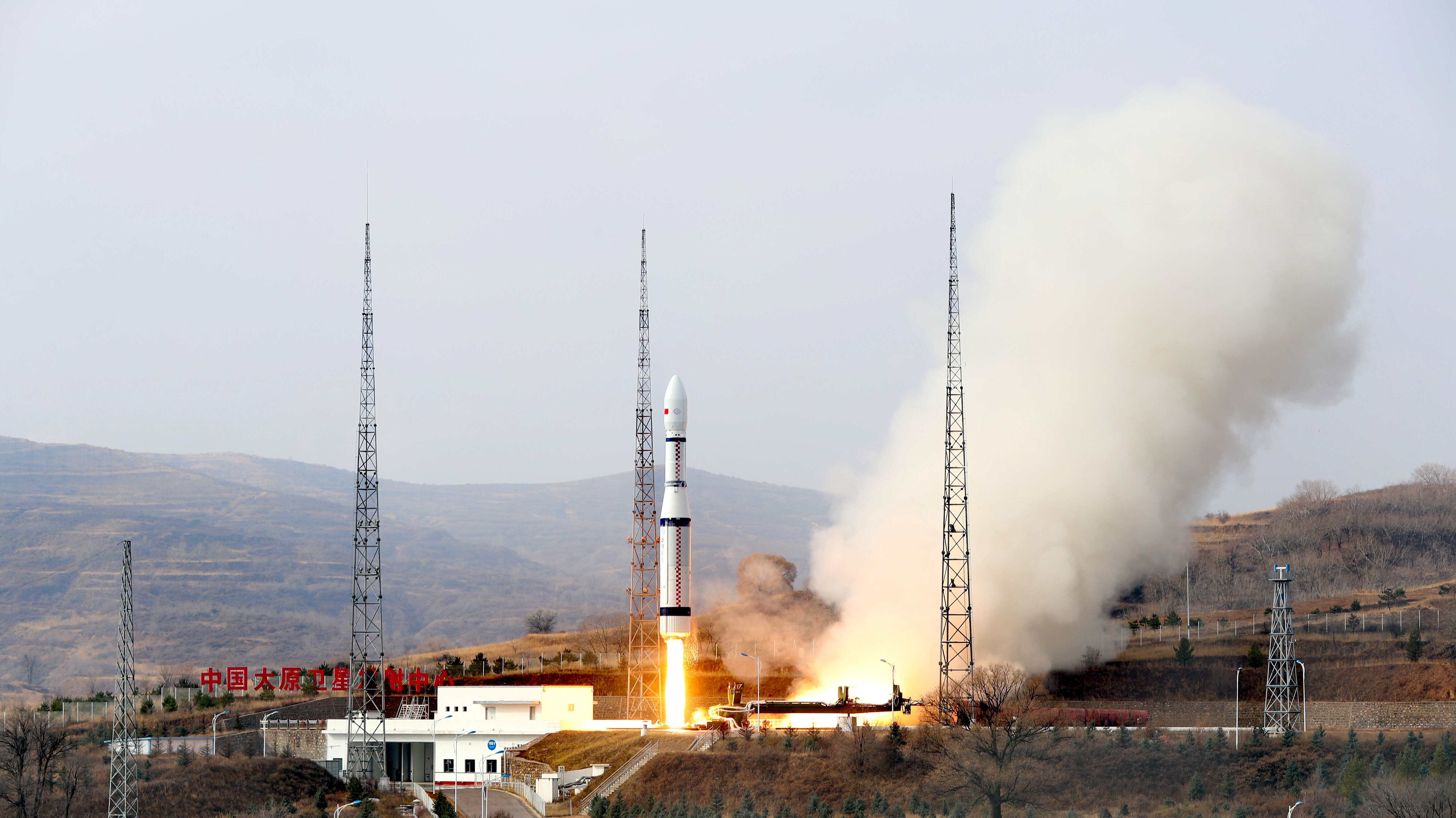 China Launches Satellite for UN Sustainable Development Goals
China Launches Satellite for UN Sustainable Development GoalsChina launched a scientific satellite that will help nations meet the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). A Long March-6 carrier rocket sent it to orbit from the Taiyuan Satellite Launch Center on Friday. Code-named "SDGSAT-1," it's the very first satellite on Earth to help realize the 17 goals in the "2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development" set by the UN in 2015 to stimulate actions in solving social, economic and environmental problems for humanity and the planet.
05 Nov 2021


