-
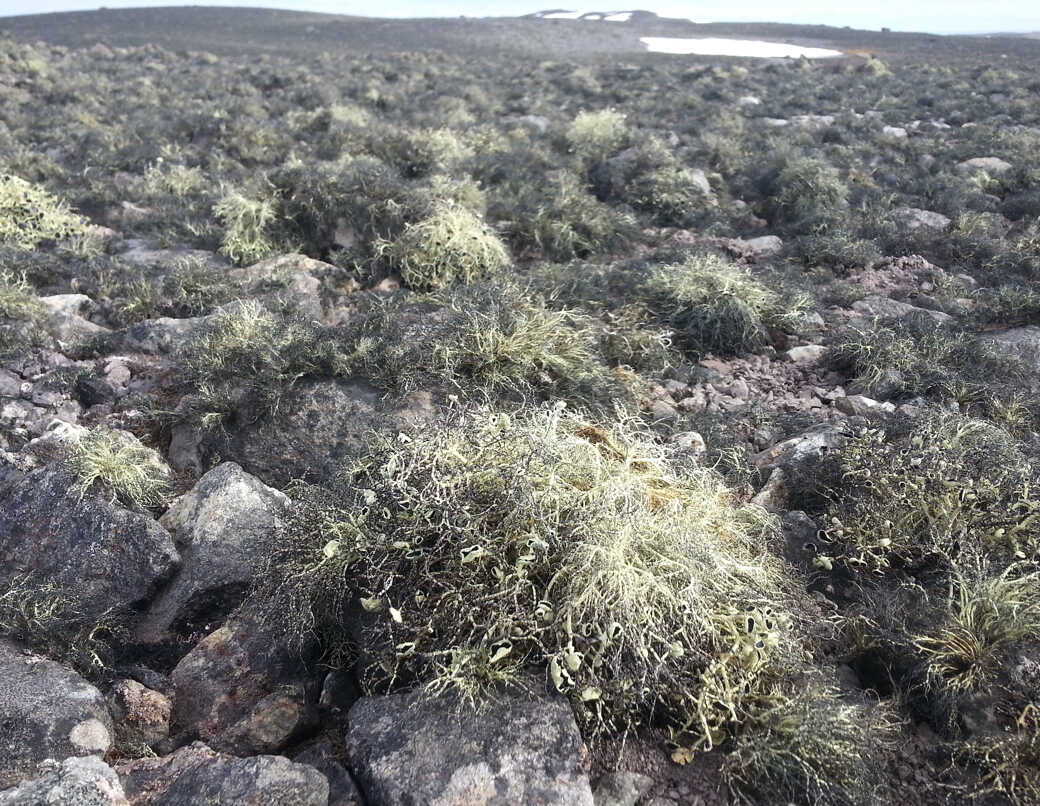 New Study Reveals How Dark-Colored Lichens Are Overlooked in Antarctic Vegetation Mapping
New Study Reveals How Dark-Colored Lichens Are Overlooked in Antarctic Vegetation MappingA research team from the Aerospace Information Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (AIRCAS), in collaboration with the Center for Advanced Studies in Earth Sciences and Biodiversity (CADIC-CONICET), Argentina, has revealed major blind spots in current Antarctic vegetation mapping caused by the poor detectability of dark-colored lichens.
12 Nov 2025 -
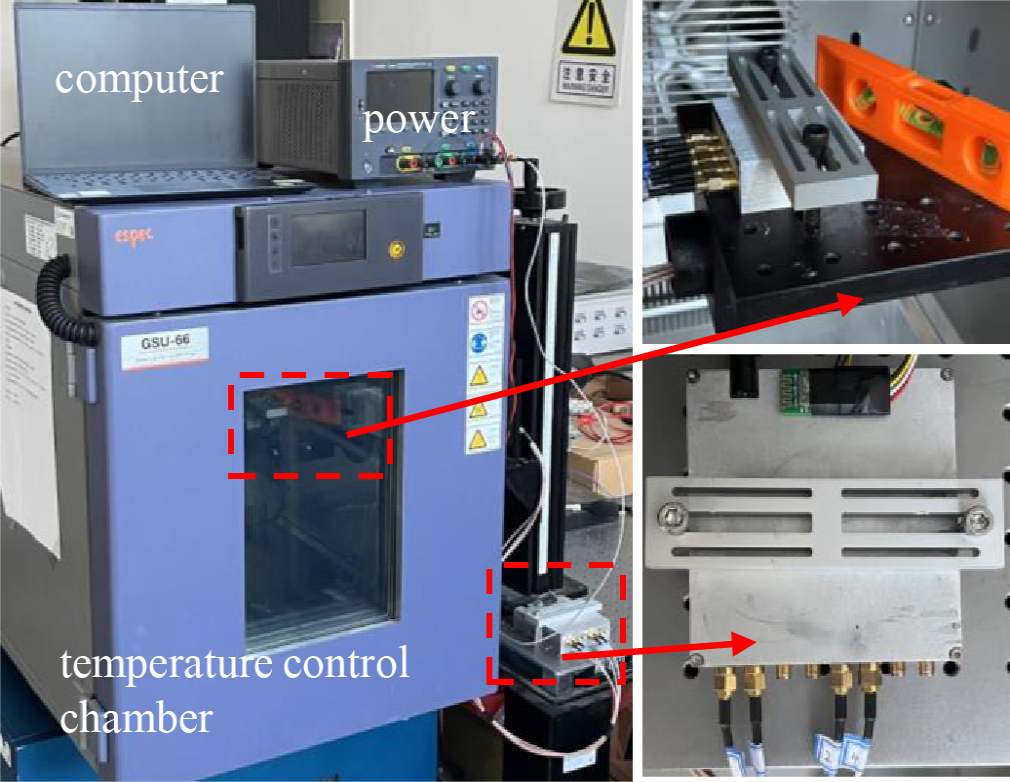 Dual-Mode Design Significantly Enhances MEMS Accelerometer Performance, Study Finds
Dual-Mode Design Significantly Enhances MEMS Accelerometer Performance, Study FindsA recent study published in Microsystem & Nanoengineering introduces an innovative solution to the persisting challenges in Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems (MEMS) resonant accelerometers: temperature drift and measurement dead zones. By adopting a dual-mode operating scheme that effectively separates the operating frequencies of the differential beams, the researchers achieved notable improvements in the sensor's accuracy and overall performances.
11 Nov 2025 -
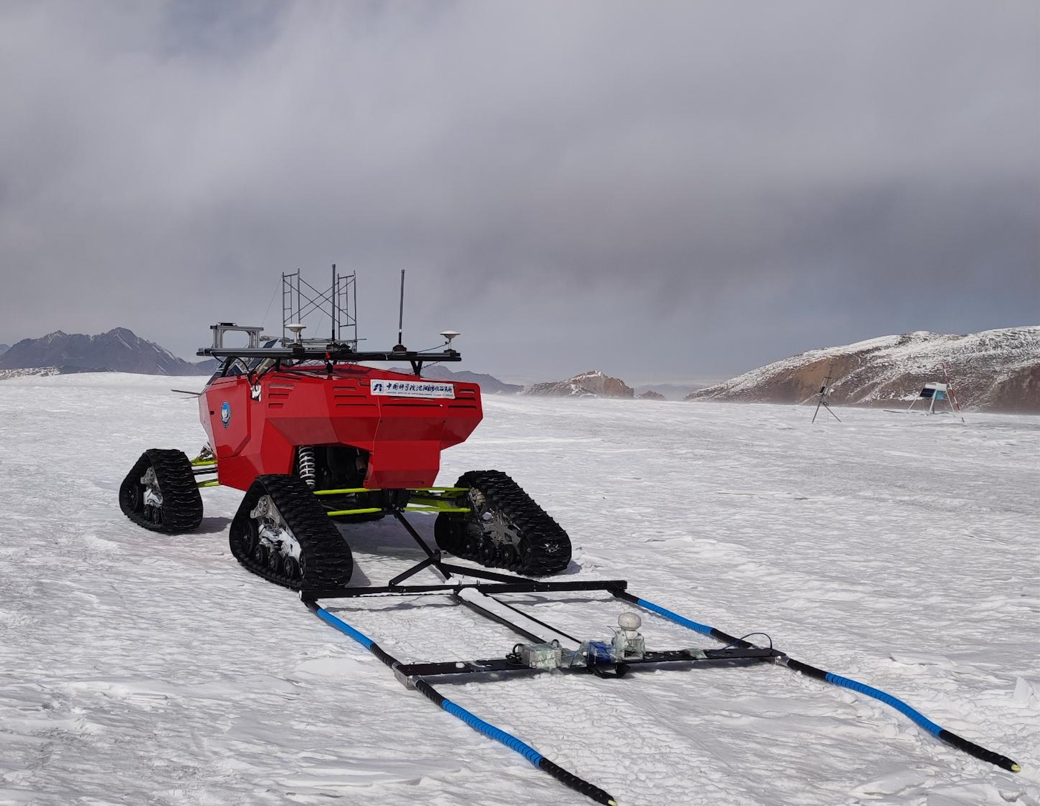 Chinese Scientists Test Unmanned Glacier Penetrating Radar on Bayi Glacier
Chinese Scientists Test Unmanned Glacier Penetrating Radar on Bayi GlacierA research team from the State Key Laboratory of Remote Sensing and Digital Earth, in collaboration with the Laboratory of Electromagnetic Radiation and Detection Technology at the Aerospace Information Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (AIRCAS), has successfully completed field testing of a self-developed unmanned vehicle-mounted glacier penetrating radar on the Bayi Glacier in the central Qilian Mountains. The tests ran from October 10 to 25, 2025.
05 Nov 2025 -
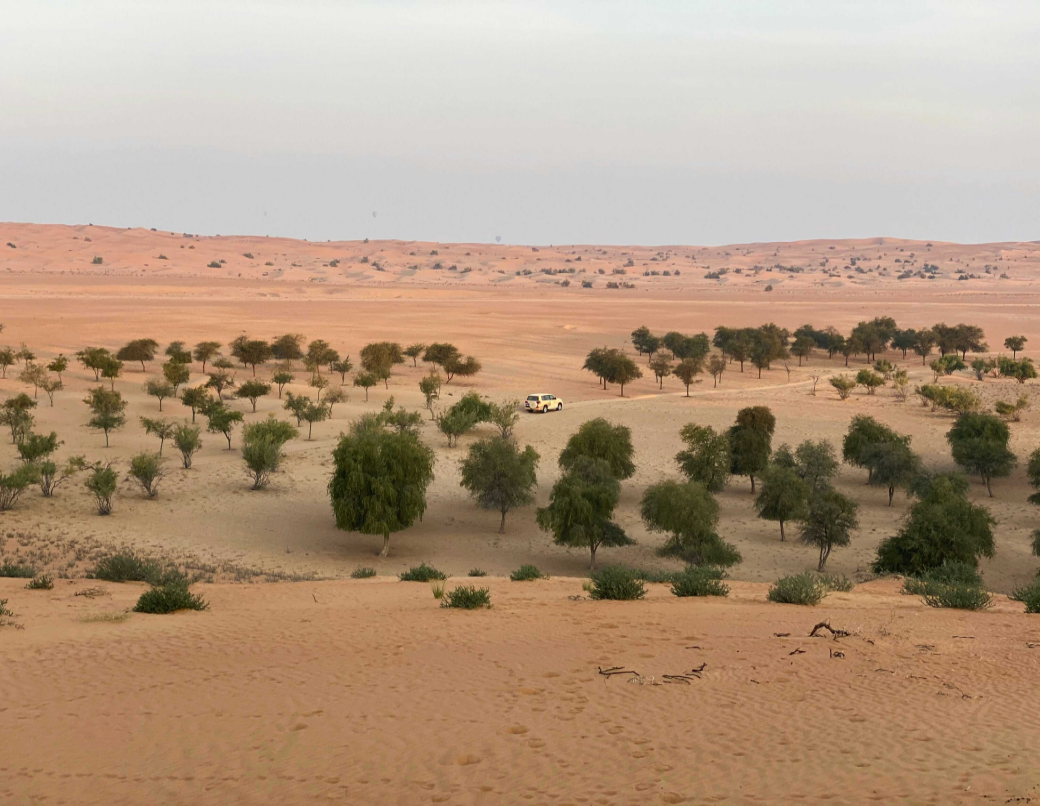 Africa's Great Green Wall Holds Great Potential for Land Degradation Neutrality, Study Finds
Africa's Great Green Wall Holds Great Potential for Land Degradation Neutrality, Study FindsA new study published in Scientific Reports has evaluated land productivity dynamics (LPD) across the African Great Green Wall (GGW) from 2013 to 2022, offered a decade-long perspective on one of the world’s most ambitious initiatives to combat desertification in the Sahel. It aims to assess progress toward the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 15.3 for Land Degradation Neutrality (LDN) and identify the key factors driving land productivity change to guide more effective restoration strategies.
31 Oct 2025 -
 Novel Field-Theoretic Framework Unlocks Universal Evolutionary Patterns of Competitive Systems in Nature
Novel Field-Theoretic Framework Unlocks Universal Evolutionary Patterns of Competitive Systems in NatureA research team from the Aerospace Information Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (AIRCAS), led by DENG Chubo and SUN Xian, has developed a field-theoretic framework to address this issue. Their findings, published in Scientific Reports, reveal that competitive systems universally converge to three distinct evolutionary regimes—Stable Equilibrium, Periodic Oscillations, or Progressive Dominance and Elimination. The discovery offers a robust theoretical tool to explain and predict antagonistic phenomena across disciplines.
31 Oct 2025 -
 Smart Satellite Tools Boost Forage Farming in Arid Lands
Smart Satellite Tools Boost Forage Farming in Arid LandsA new study in Water Research presents an artificial intelligence (AI)-powered remote sensing framework to precisely map forage cultivation potential across northern China's hs, especially the middle reaches of the Yellow River. This study identified optimal forage belts at the kilometer scale, offering robust data and decision-ready tools to support ecological protection, sustainable agriculture, and national feed and food security.
27 Oct 2025


