-
 Digital Earth Symposium Opens in Chongqing with Focus on SDGs
Digital Earth Symposium Opens in Chongqing with Focus on SDGsThe 14th International Symposium on Digital Earth opened on Monday in Chongqing, drawing nearly 700 delegates from 30 countries and regions to discuss how digital technologies can help accelerate progress toward the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals.
25 Apr 2025 -
China Focus: China Strengthens Space Technology Cooperation with Global South Nations
BEIJING, April 25 (Xinhua) -- In the second week of April, Lusaka became a hub of agricultural innovation as technicians from Southern African countries gathered for a unique three-day training session. Unlike typical workshops, this one provided a customized experience. Participants brought data from their own countries and practiced on the satellite remote sensing agricultural monitoring platform developed by Chinese scientists, tailoring their learning to fit local needs. This exemplified China's increasing collaboration with Global South countries in space technology -- not merely through memorandums or broad agreements, but by translating cutting-edge innovation into tangible, real-world applications.
25 Apr 2025 -
Space 2.0: Big Data, Big Debris, and the Battle for Sustainability
As the space race hots up once again, representatives of over 50 countries are at the Farnborough International Space show to focus on sustainability. Just how can science, data, and technology drive sustainable progress, not just on Earth but beyond?
01 Apr 2025 -
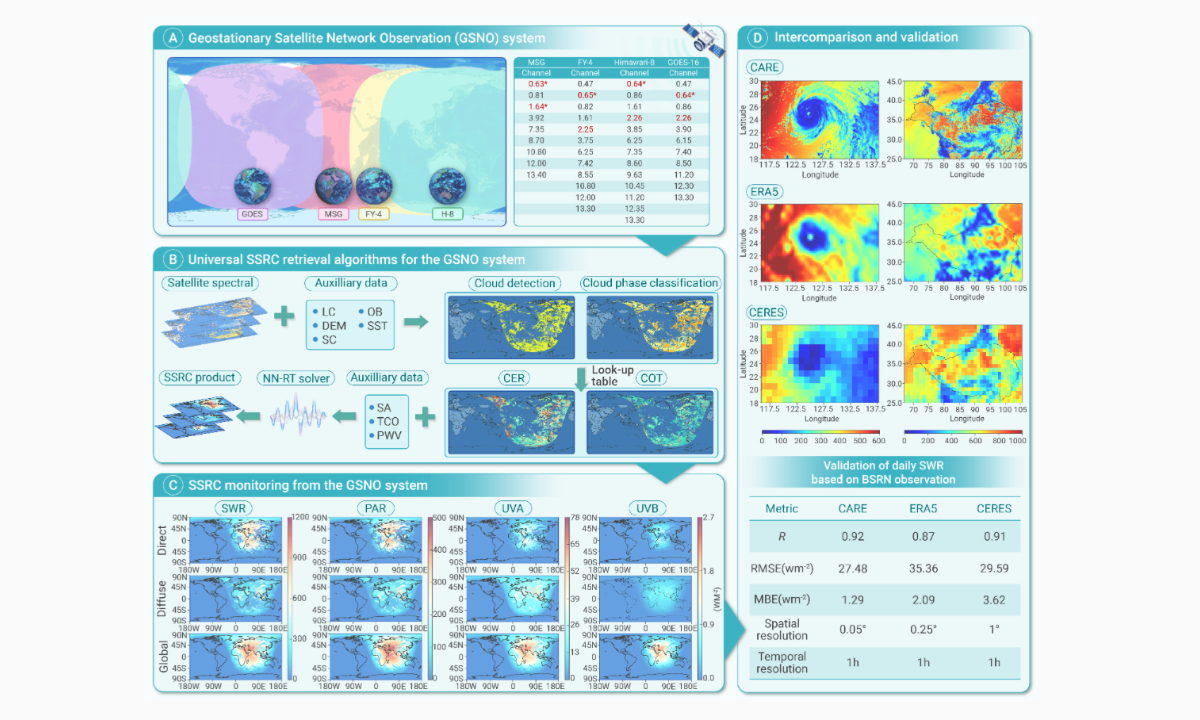 Chinese Scientists Lead Construction of High-precision Monitoring System for Near-global Surface Solar Radiation
Chinese Scientists Lead Construction of High-precision Monitoring System for Near-global Surface Solar RadiationChinese scientists, in collaboration with several international research institutions, have led the construction of a high-precision surface solar radiation monitoring system on a near-global scale. The joint research led by researchers from the State Key Laboratory of Remote Sensing and Digital Earth of the Aerospace Information Research Institute under the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with scientists from Japan, France the UK has recently been published in the international academic journal The Innovation.
01 Apr 2025 -
 Breakthrough in Deep Ultraviolet Laser Technology
Breakthrough in Deep Ultraviolet Laser TechnologyAs reported in Advanced Photonics Nexus, researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences recently made a significant advancement by developing a compact, solid-state laser system capable of generating 193-nm coherent light. This wavelength is crucial for photolithography, a process used to etch intricate patterns onto silicon wafers, forming the backbone of modern electronic devices.
24 Mar 2025 -
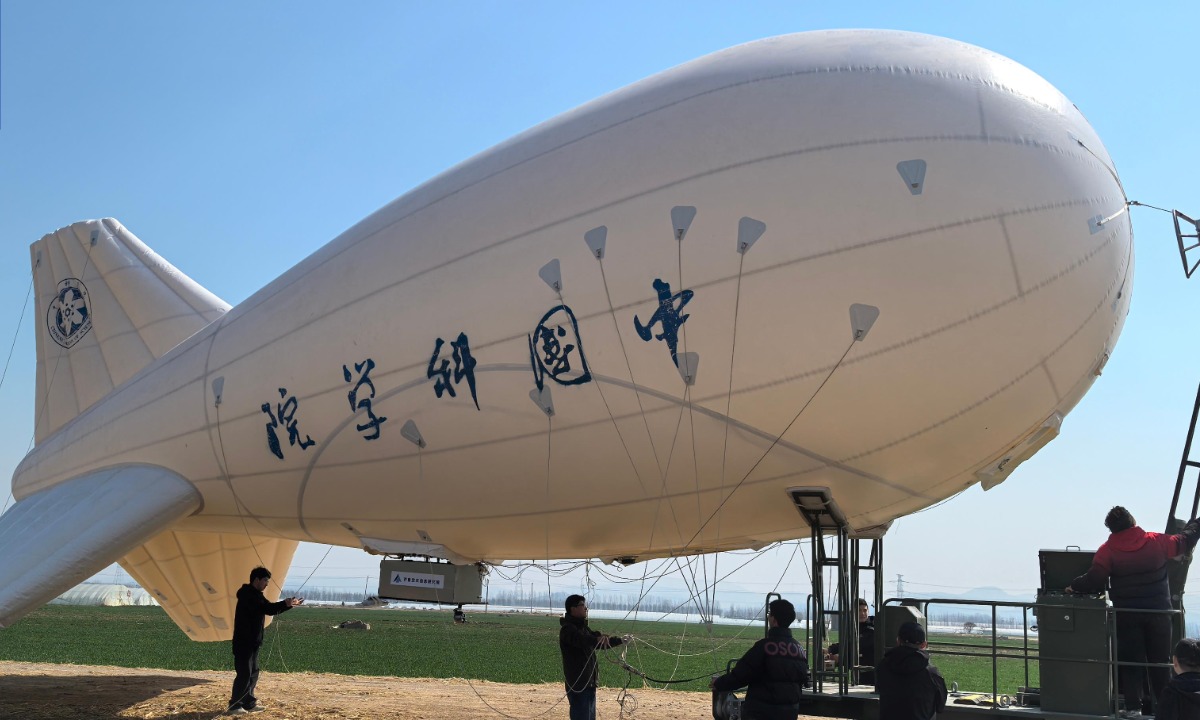 Chinese Research Institute Unveils Aerial Balloon Platform to Bolster Energy Development
Chinese Research Institute Unveils Aerial Balloon Platform to Bolster Energy DevelopmentA tethered balloon, developed by the Aerospace Information Research Institute (AIR) under the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), was successfully deployed on Wednesday to assist in the construction of ultra-high voltage (UHV) transmission lines in Tai'an city, East China's Shandong Province. This marks China's first use of an aerial platform for energy projects, the CMG reported.
20 Mar 2025


