Scientists Propose Global Aerosol Retrieval Method for New Chinese Optical Satellite
Jul 21, 2023
Aerosols, suspended particles in the atmosphere, are known to influence the Earth's climate system by directly scattering and absorbing solar and terrestrial radiations as well as by acting as cloud condensation nuclei and ice nuclei to modify the properties of clouds.
Newly launched satellite sensors often face challenges in obtaining sufficient observations in a short period to support the development of land surface reflectance (LSR) constraints for aerosol retrieval.
A research team led by Prof. LI Zhengqiang from the Aerospace Information Research Institute (AIR), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), together with collaborators, proposed a generalized land surface reflectance reconstruction method that provides efficient constraints to surface reflectance for high-precision aerosol retrieval.
The study “A generalized land surface reflectance reconstruction method for aerosol retrieval: Application to the Particulate Observing Scanning Polarimeter (POSP) onboard GaoFen-5 (02) satellite” is recently published in Remote Sensing of Environment.
Based on the reference surface reflectance product, the proposed method only needs a short time observation of the target sensor, and it uses the spatial-temporal minimum reflectance technology to implement reconstruction of the long-time historical surface reflectance product of the reference sensor. Then the reconstructed virtual LSR can be used to construct reliable surface constraints for high-precision retrieval of aerosol parameters.
This method has been successfully applied to the Particulate Observing Scanning Polarimeter (POSP) onboard Gaofen-5 (02) satellite. The researchers found using the overlapping observations of POSP and MODIS for only one month, a stable surface reflectance reconstruction relationship between the two could be established. And the retrieved aerosol optical depth (AOD) based on the reconstructed LSR achieved a very high accuracy level according to the validation results against AERONET observations.
The research has made breakthroughs in the ability of fast surface-atmosphere decoupling and global aerosol retrieval for new Chinese optical satellites.
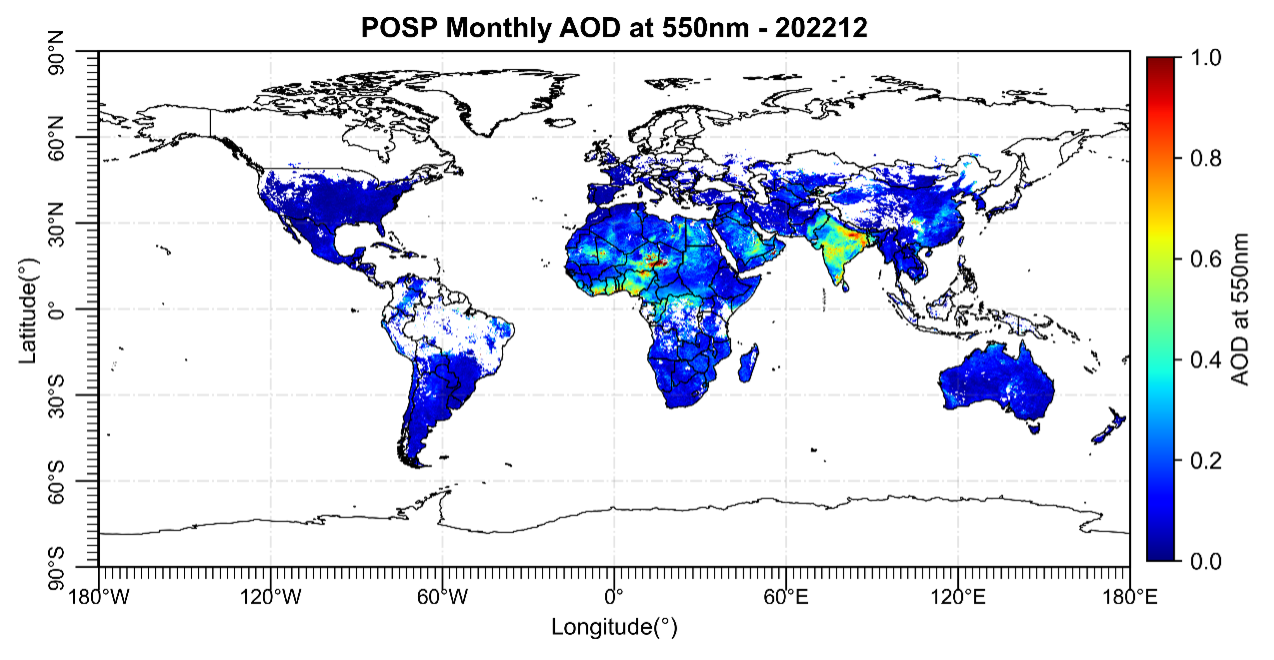
Global AOD distribution obtained by POSP/Gaofen-5 (02). (Image by AIR)
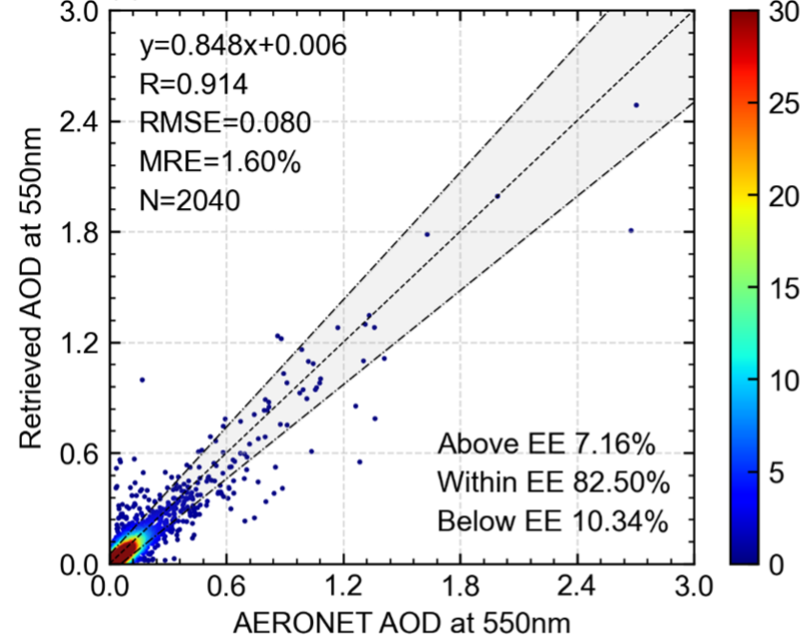
Validation of POSP AOD with AERONET data. (Image by AIR)
Contact: luyq@aircas.ac.cn



News & Events